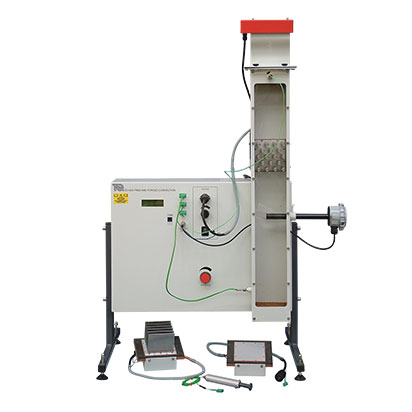
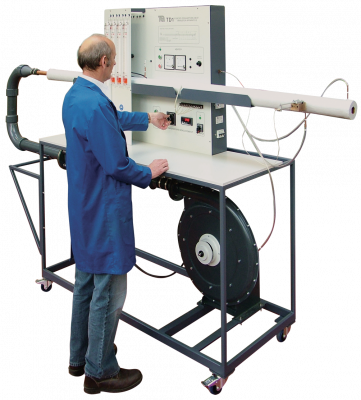
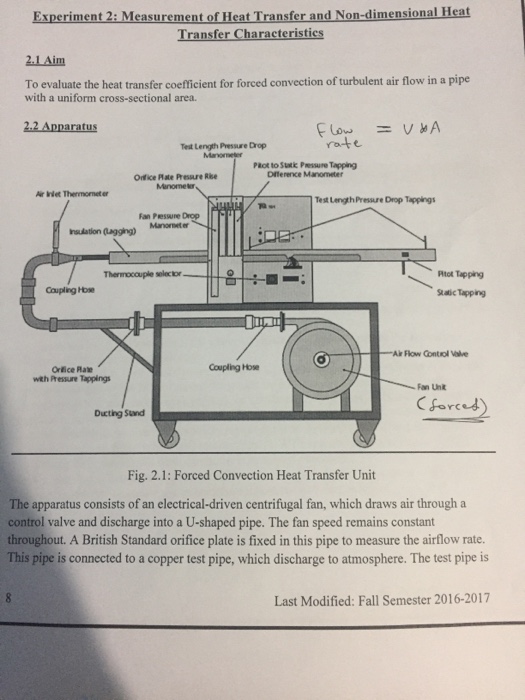
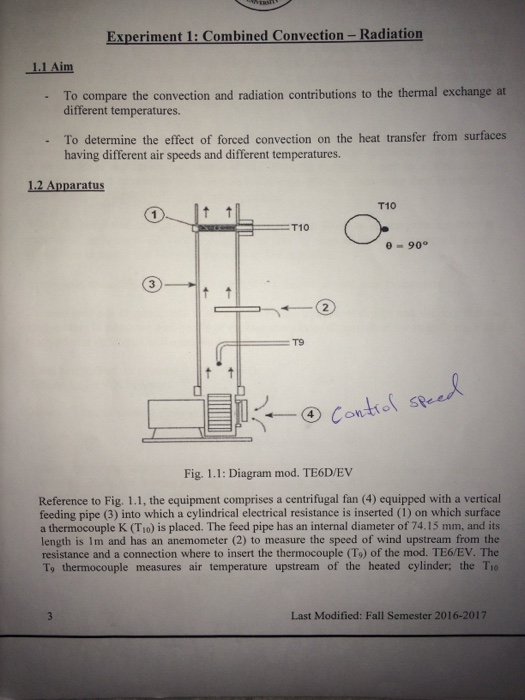
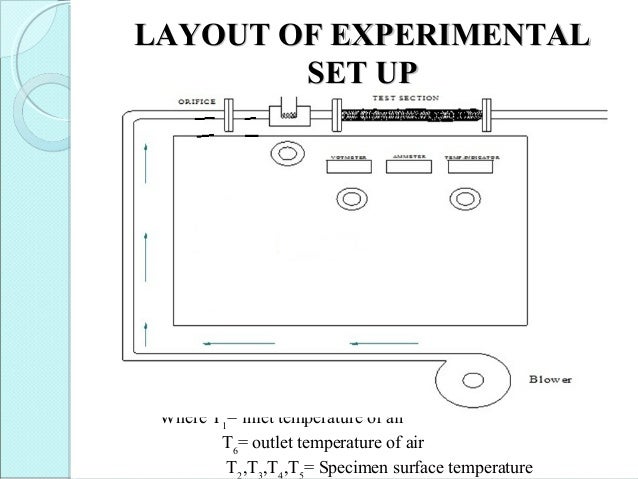
Forced Convection Heat Transfer Experiment

The high velocity fluid results in a decreased thermal resistance across the boundary layer from the fluid to the heated surface.
Forced convection heat transfer experiment. Convection is classified as natural or free and forced convection depending on how the fluid motion is initiated. The forced convection setup results in an increase in dissipated heat in the exiting of the fluid into the. An experimental study of forced convective heat transfer from smooth solid spheres 1. The convective heat transfer measurement system is an experimental apparatus for measuring forced and natural convection heat transfer for external flows over surfaces of various geometries.
Forced convective heat transfer from spherical objects or objects that are modelled as spheres is. Alfonso figueroa in partial fulfillment of the requirements of che 352 spring semester 2015 arizona state university chemical engineering program abstract forced convection is a process that is used in determining heat transfer coefficients of different types of materials. This in turn increases the amount of heat that. For free convection tests the heated air rises from the surface and up the duct.
3 6 l i 6 1. Thermocouples measure the air temperature upstream and downstream of the surface and the temperature at the heat transfer surface. The rise of warmer fluid and fall the cooler fluid. Tecquipment s forced convection heat transfer apparatus allows students to examine the theory and associated formulae related to forced convection in pipes.
Forced convection a research report submitted by. It also has a large work surface for student convenience. A sketch of the basic apparatus for forced convection measurement is shown in figure 3 and a cut away. The principle of heat transfer by thermal convection is that the hot particles flow from a point a to b over a macroscopic distance.
In the next section of the report the procedure used to complete the actual experiment is shown. In the forced convection the fluid to be heated is blown or pumped past the heated surface by employing a pump or a fan while in the natural or free convection fluid flow is naturally achieved based on the density variation in the heated fluid. The heat transfer rate to the fluid 3 6 can be calculated using the fist law of thermodynamics for the heated fluid. The employed test facility is described in section 2 1.
This results in a larger total heat transfer for the forced convection than the free convection. In natural convection any fluid motion is caused by natural means such as the buoyancy effect i e. In this case heat flows along with the substance so to speak. Heat transfer by forced convection generally makes use of a fan blower or pump to provide high velocity fluid gas or liquid.
Convection is the mechanism of heat transfer through a fluid in the presence of bulk fluid motion. For forced convection tests a variable speed fan draws air up through the duct and across the surface.