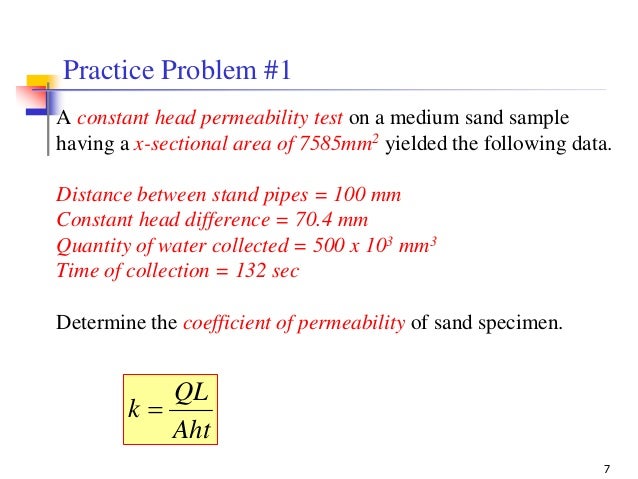
Constant Head Permeability Test Problems

This part describes the method for determination of coefficient of permeability of granular soils by a constant head method and under conditions of laminar flow of water.
Constant head permeability test problems. The soils that are suitable for this tests are sand and gravels. Fix the drainage cap. Constant head permeability test results. Recordings during constant head permeability test 6.
Quantity of water that will flow toward an excavation design of cutoffs beneath dams on permeable foundations design of the clay layer for a landfill liner. Permeability at temperature k t is calculated by. It directly affects the following. For fine grained soil falling head permeability test is done whereas constant head permeability test is done for the coarse grained soil.
Now a falling or constant head permeability test may be conducted depending on the type of soil. The falling head test is mainly used for less permeable soils k 10 4 cm s. The constant head permeability test follows the principle of darcy s law and therefore it is recommended by the aci. The knowledge of this property is essential in a solution of problems involving de watering yield of water bearing strata seepage through earth dams etc.
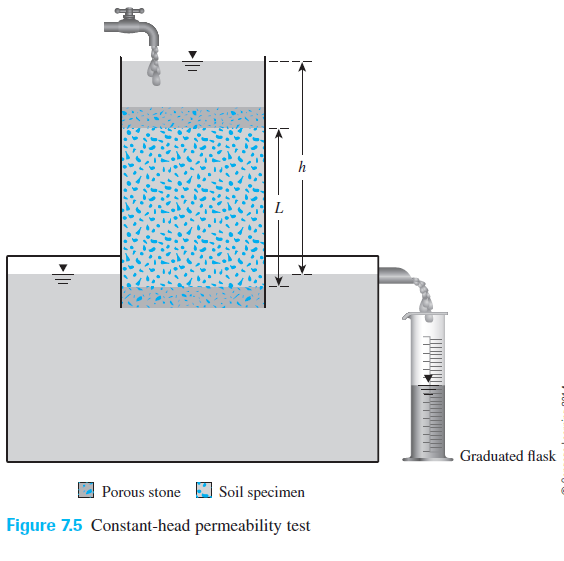
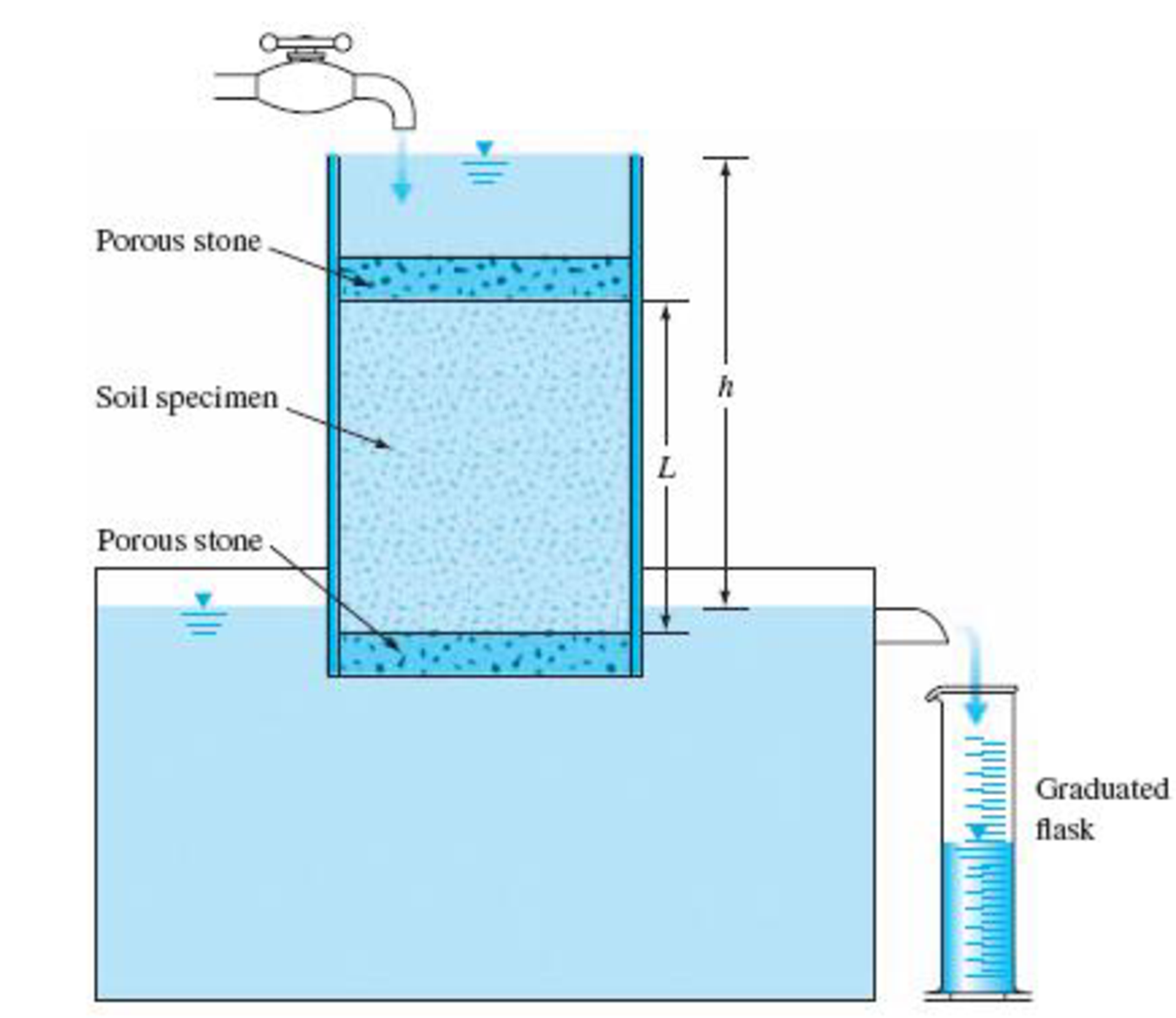
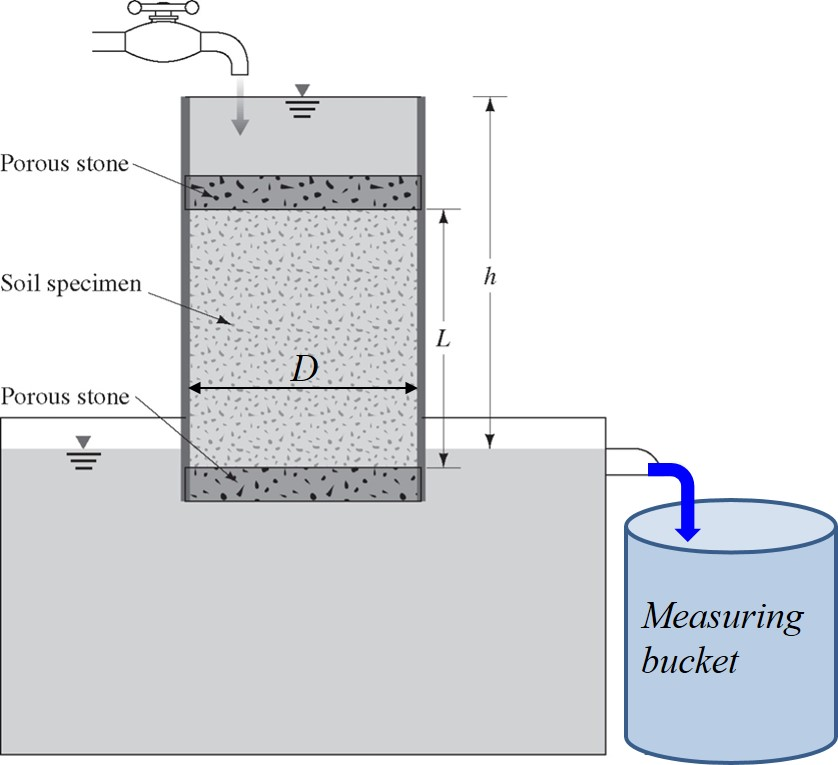
There are two general types of permeability test methods that are routinely performed in the laboratory. Constant head objective to determine the coefficient of permeability of a soil using constant head method. In that regard the test measures the amount of water that goes through a sample in a determined time. Determine the coefficient of permeability for the tested soil.
The applied test is an adaptation of the one suggested by several authors always respecting the constant head. The constant head test method and 2 the falling head test method. K t q a x i x t and permeability at 27 c by using the expression k 27 k t x μ t μ 27 where μ t coefficient of viscosity at t 0 c μ 27 coefficient of viscosity at 27 0 c. The constant head permeability test is usually preferred for sandy soils and the variable head permeability test for silty and clayey soils.
Soils with silt content cannot be tested with this method the test can be employed to test granular soils either reconstituted or disturbed. 6 1 constant head test. Need and scope the knowledge of this property is much useful in solving problems involving yield of water bearing strata seepage through earthen dams stability of earthen dams and embankments of canal bank affected by seepage settlement etc. 20 cubic inches soil uscs classification.
The constant head test method is used for permeable soils k 10 4 cm s and. Length of sample l 12 inches sample diameter cylindrical sample 2 0 inches constant head difference 2 5 feet volume of water collected in 5 minutes.